Grid orientations
[Combinatoric Algorithms on Grids]
Algorithms related to orientation of grids.
More...
Collaboration diagram for Grid orientations:

|
Functions | |
| template<class G , class GT > | |
| bool | GrAL::get_orientation (G const &g, GT &orientation) |
| Determine relative orientation of cells. | |
| template<class G , class C > | |
| bool | GrAL::fix_orientation (G &g, C guide_cell) |
| Change orientation of cells such that it is consistent. | |
| template<class G > | |
| bool | GrAL::fix_orientation (G &g) |
| Convenience wrapper for orientation. | |
Detailed Description
Algorithms related to orientation of grids.Function Documentation
template<class G , class GT >
| bool GrAL::get_orientation | ( | G const & | g, | |
| GT & | orientation | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Determine relative orientation of cells.
- Template parameters:
G- Model of CellRange
- type
FacetOnCellIterator - The function
int relative_orientation(FacetOnCellIterator f1, FacetOnCellIterator f2)has been overloaded forG::FacetOnCellIteratorand returns the relative orientation of the facet*f1 == *f2induced byf1andf2. For instance, in a 2D grid, this means that if the edge*f1is represented with opposite vertex ordering byf1andf2, the result should be -1, and +1 otherwise.
GF- Model of cell based MutableGridFunction
- Parameters:
-
g input grid orientation output grid function indicating orientation changes
- Returns:
- true if the grid is orientable, and false otherwise.
- Precondition:
gis a manifold-with-boundary gridorientationis bound tog
- Postcondition:
- On return,
orientation(c)is positive if the orientation does not need to be changed, and negative otherwise. The absolute value oforientation(c)indicates the connected component ofc.
- Note:
- The orientation flags in
orientationare computed on a purely combinatorial basis. If an orientation with a geometric meaning is wanted (e.g. producing outward pointing normals in the case of a manifold grid embedded in andim(g)+1dimensional space, one has to flip, orientations of either all cells with positive or all cells with negative flags, for each component independently.
- See also:
- Tested in test-orientation.C
Definition at line 76 of file orientation.h.
References relative_orientation().
Referenced by GrAL::fix_orientation().
template<class G , class C >
| bool GrAL::fix_orientation | ( | G & | g, | |
| C | guide_cell | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Change orientation of cells such that it is consistent.
- Template parameters:
G- Model of CellRange
- type
FacetOnCellIterator - function
swap_orientation(Cell) - The function
int relative_orientation(FacetOnCellIterator f1, FacetOnCellIterator f2)has been overloaded forG::FacetOnCellIteratorand returns the relative orientation of the facet*f1 == *f2induced byf1andf2. For instance, in a 2D grid, this means that if the edge*f1is represented with opposite vertex ordering byf1andf2, the result should be -1, and +1 otherwise.
C
- Model of GridCell
- Parameters:
-
g input grid, orientation of some cells will be changed on output \c guide_cell Cell with reference orientation
- Returns:
- true if the grid is orientable, and false otherwise.
- Precondition:
gis a manifold-with-boundary gridc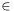
g
- Postcondition:
- On return,
gis oriented consistent withguide_cell, such that a call toget_orientation(g, orient)will yieldorientation(c) == 1for each cellcofg.
- See also:
- Tested in test-orientation.C
- Todo:
- Extend to list of guide cells for disconnected grids.
Definition at line 154 of file orientation.h.
References GrAL::get_orientation().
Referenced by GrAL::fix_orientation().
template<class G >
| bool GrAL::fix_orientation | ( | G & | g | ) | [inline] |
Convenience wrapper for orientation.
Equivalent to fix_orientation(g, * g.FirstCell())
Definition at line 173 of file orientation.h.
References GrAL::fix_orientation().
 1.5.8
1.5.8